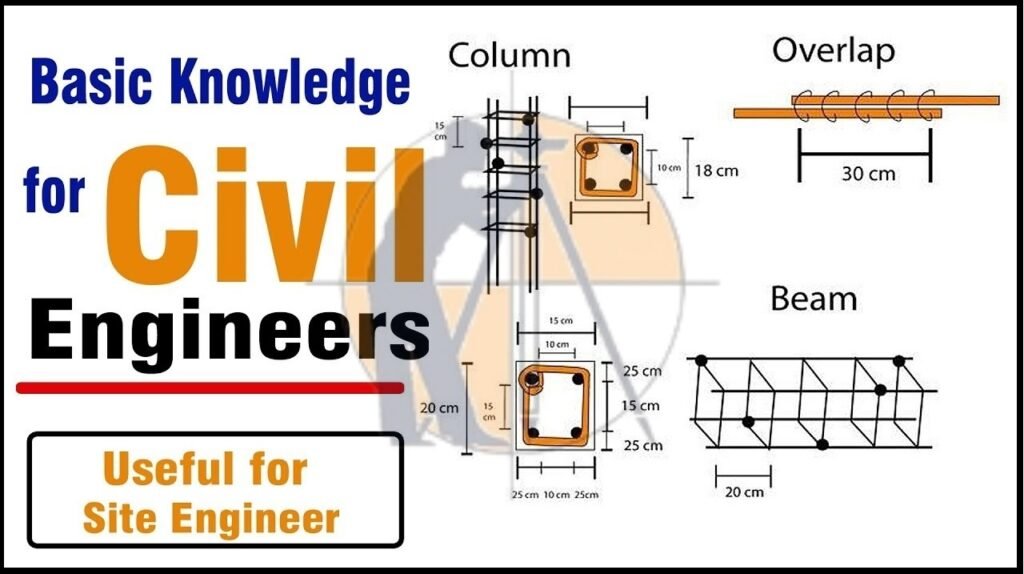
Civil Engineering Basic Site Knowledge.
Useful Information For Land Surveyors And Civil Engineers. Get Benefits And Share With Others.
-
Definition and Scope:
Civil engineering is a branch of engineering that deals with the design, construction, and maintenance of infrastructure, including buildings, bridges, roads, dams, and other large-scale projects essential for society’s functioning.
-
Core Areas of Study:
- Structural Engineering: Focuses on the design and analysis of structures to ensure they can withstand loads and environmental factors.
- Geotechnical Engineering: Deals with soil and rock mechanics, foundation design, and slope stability analysis.
- Transportation Engineering: Involves the planning, design, and operation of transportation systems, including roads, railways, airports, and ports.
- Environmental Engineering: Addresses environmental issues related to infrastructure projects, such as water and air pollution control, waste management, and sustainable development.
- Hydraulic Engineering: Concerns the management of water resources, including the design of dams, channels, and flood control systems.
- Construction Engineering: Involves project management, construction methods, materials, and equipment selection, and ensuring projects are completed safely, on time, and within budget.
-
Key Concepts:
- Load and Stress: Understanding how loads are transferred through structures and how they affect the materials used.
- Material Properties: Knowledge of the properties of construction materials like concrete, steel, wood, and asphalt.
- Surveying: Techniques for measuring and mapping land and infrastructure features to aid in design and construction.
- Codes and Standards: Familiarity with building codes, regulations, and industry standards to ensure compliance and safety.
- Cost Estimation: Techniques for estimating project costs, including materials, labor, and equipment.
-
Tools and Technologies:
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD): Software used for drafting and designing infrastructure projects.
- Building Information Modeling (BIM): Digital representations of physical and functional characteristics of buildings and infrastructure.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Tools for analyzing and managing spatial data related to infrastructure planning and management.
- Structural Analysis Software: Programs for simulating and analyzing the behavior of structures under various conditions.
-
Career Opportunities:
Civil engineers work in various sectors, including government agencies, consulting firms, construction companies, and research institutions. They may specialize in specific areas such as transportation, water resources, or structural design.
This overview provides a foundation for understanding the field of civil engineering and its essential concepts, disciplines, and applications.
Learn More
How To Import Points Create Surface And Calculate Volume in Auto Cad Civil 3D
1. Structural Engineering :
This branch focuses on the design, analysis, and construction of structures to withstand various loads and environmental conditions. It includes buildings, bridges, dams, towers, and other infrastructure. Engineers in this field use principles of mechanics, materials science, and structural analysis to ensure the safety and stability of these structures.
2. Geotechnical Engineering:
Geotechnical engineering deals with the behavior of earth materials such as soil and rock. It involves assessing the properties of these materials to determine their suitability for construction projects, as well as designing foundations, slopes, and retaining structures to support built infrastructure.
3. Transportation Engineering:
Transportation engineering involves the planning, design, and operation of transportation systems such as roads, railways, airports, and ports. Engineers in this field work to optimize traffic flow, improve safety, and enhance the efficiency of transportation networks.
4. Environmental Engineering:
Environmental engineering focuses on the protection and enhancement of the environment through the management of water resources, waste disposal, pollution control, and sustainable development practices. It addresses issues such as water and air quality, wastewater treatment, and solid waste management.
5. Water Resources Engineering:
This branch deals with the planning, management, and development of water resources such as rivers, lakes, groundwater, and reservoirs. Water resources engineers work on projects related to flood control, irrigation, water supply systems, hydropower generation, and watershed management.
6. Construction Engineering:
Construction engineering involves the planning, coordination, and execution of construction projects. It encompasses project management, cost estimation, scheduling, quality control, and safety management to ensure that construction projects are completed efficiently and within budget.
7. Materials Engineering:
Materials engineering focuses on the selection, testing, and application of construction materials such as concrete, steel, asphalt, and composites. Engineers in this field study the properties and behavior of materials to ensure their suitability for specific applications and to optimize the performance of civil engineering structures.
These are just a few of the key areas within civil engineering, and there are many other specialized fields and interdisciplinary areas that civil engineers may work in, depending on their interests and expertise.
Learn More
What Is Difference between Site Engineer and Civil Supervisor
What is the Difference between main bars and distribution bars in slab
Learn More
How to calculate the RL of temporary benchmark on the site
How To Calculate The Asphalt Quantity For Road Work
Learn More
How to calculate the self weight of RCC footing And plinth beam
How to Calculate the Quantity of Cement Mortar In Brickwork and Plaster