Components of the Road Structure
What is the Components of Road structure?
In this article i will Explain about components of the roads and the structure of roads and it is composition after reading this article u will understand a lot of about components of the road structures. I will try to make it as simple it can be.
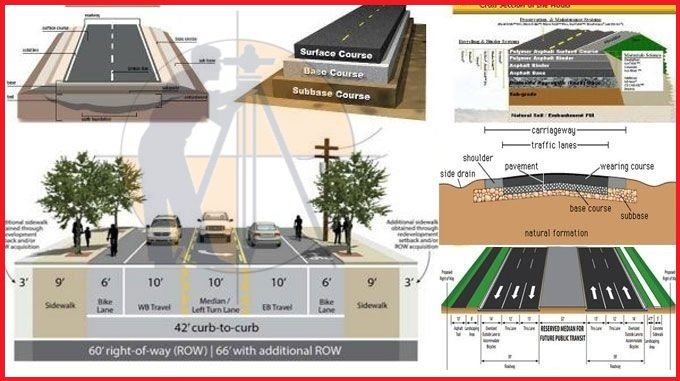
There are few component of the road structure which are going to be discuss below which are as follows:
-
CARRIAGEWAY
-
FORMATION WIDTH
-
KERB
-
ROAD MARGIN
-
MEDIANS
-
CAMBER
-
RIGHT OF WAY
1 – Carriage Way
The Carriageway is the width of the road on which traffic moves without any restriction.it generally consist of the traffic lines and the width of the carriageway depend on the lines of traffic. Traffic lines are those lines on which traffic can move freely without any restriction. Each country has its own rules for the width of the carriageway for insistence how long should it be in some country for the single line road its 2.44m in some its more than that for 2 line its 3.75m in some more then that.
Learn More
How To Convert the Bearings and Distances to Coordinates
Interview Question and Answer For Land Surveying
Long Wall And Short Wall Method
2 – Formation Width
The formation width of the road is the sum of carriageway, shoulders & separators (if there is any).
3 – Kerb
Kerb is the boundary line formed from stone or concrete block which separate carriageway form the footpath. There are different types of the kerb with different types of height. There are 4 type of kerb which are low or mountable Krebs, semi-barrier kerb, barrier kerb, & submerged kerb. Iow kerbs are used for traffic to remain in the line and also separate the shoulder from the road so the driver can enter the shoulder area with little difficulty it is height is ten cm (Four inch). The semi barrier kerb has height of Fifteen cm (Six inches). Barrier kerbs has a height of 20cm (Eight inch). They are provided where pedestrian traffic is in considerable amount. Submerged kerb are used in the rural roads the basically provide stability to the road pavement.
4 – Road Margin
The part of the road except carriageway are usually called road margin, it includes different parts or element of the road which are given below
-
Shoulders.
-
Bus bays.
-
Parking lines.
-
Sidewalks or footpaths.
-
Service roads.
-
Cycle track.
-
Guard rails.
-
Drive way.
-
Frontage roads.
1 – Shoulders
The Shoulders is a part of the formation width except carriage way. Provided alongside the carriageway it’s basically the road for an emergency use for ambiance in rush hour or to stop the vehicle for repairing propose, and it can be used for the extension of the road in future. The width of the shoulders is kept in between 2.5 m to 4.6 m.
2 – Bus Bays
Bus bays or bus stops are stationed on side of the road where the bus can stop safely to pick up passengers or drop off without disturbing the traffic flow they are provided at least Seventy five m (250 feet) away from intersection of the road.
3 – Parking Lines
In the urban roads they usually provided parking on the road side and parallel parking is preferred because it does not disturb the traffic flow. Its width is three m(Ten feet).
4 – Sidewalks or Footpath
The Sidewalks and footpath is the same word When there is heavy amount of traffic & pedestrian flow a special paved area is provided for the pedestrian to walk safely on it without any accident.
Learn More
Calculate The Staircase Shuttering Quantity
How to Import Points Create Surface and Calculate Volume In AutoCAD Civil3D
Tendering methods and Procedures in Construction
Calculate the weight of different types of steel
5 – Service Road
The Service roads are provided parallel to the main road & also connect to the main highway, expressway. They are separated from the main road and are connected to the highway at selected points. They are provided to not disturb the traffic flow.
6 – Cycle Track:
The Cycle track are provided in those areas where the cycle traffic volume is high than width of the cycle track is kept between two to three m or in other words (Six to Ten feet).
7 – Guard Rails
The Guard rails are usually provided on the shoulder of the road. If the fill is more than three m (ten feet) they are provided. Their main is purpose to restrict them from falling of the road & to prevent them from serious accident. The Guard rails are made of different types and in the different shapes they are either made of steel, concrete or stone. They are painted white or yellow for the better visibility.
5 – Medians
The Medians are provided to isolate traffic. Their main area purpose is to restrict the collision of the traffic that are moving in opposite direction of 1 another.
6 – Camber
The Camber or cross slope is provided in the middle of the road or carriageway for the drainage of rain water form the road surface. The main purpose of the camber is to prevent water from entering to the subgrade of the road, the road quickly dries which prevent the traffic from slipping off road which decrease the accident rate. The height of the camber depends upon the material of the road and the intensity of rain fall in the region. The value of camber varies from One to 25 or one to 50.
6 – Right of Way
The Right of way is the total land require for the construction of the road. Which include carriages way, foot path, and the future extension. The right of the way depends upon the importance of the road for the future extension.
Learn More
How to calculate the Quantity of Earthwork in the Road
Standard Brick Dimensions
What is The Contour Mapping
Types Of Curves In Surveying Work
Quality Control Engineer Interview Question And Answer
8 – Drive Way
The Drive way join the highway with commercial organizations or buildings such as gas station, filling station, gasoline station, petrol station etc.
9 – Frontage Roads
The Frontage Roads is constructed to give acquire properties along an essential highway. It may be run parallel to the highway and the segregated by separators.
 Surveying & Architects A unique platform of Civil Engineering
Surveying & Architects A unique platform of Civil Engineering
