Practical And Basic Knowledge of Civil Engineering
In this Article today we will talk about the Civil Engineering Basic Knowledge | Civil Engineering Tips | Civil Engineering Notes | Civil Engineering Formulas | Practical Knowledge of Civil Engineering.
Civil Engineering Basic Knowledge, There are many activities that should be performed by civil engineer at site and in lab. Here we are going to discuss some important points which every civil engineer must learn and remember. These tips can also helps to crack interview. This is a kick start guide if you are joining in a any company as a Civil engineer and these are the best Civil Engineering Tips.
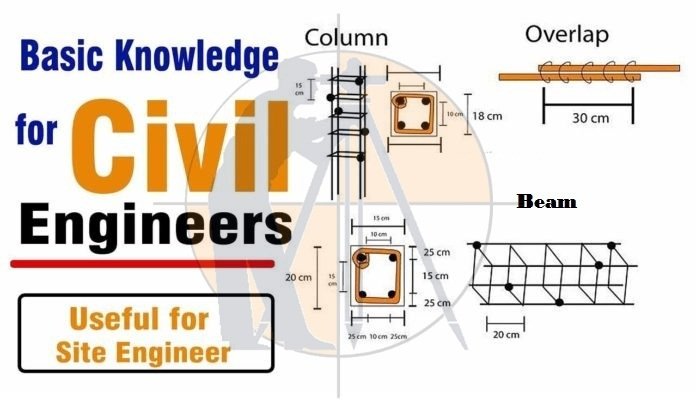
Civil Engineering Basic Knowledge for Cement:
- Grade of concrete is denoted as cement, sand, Aggregate.
- The initial setting time shall not be less than 30 minutes and the final setting time of cement is 10 Hours. Practical Knowledge of Civil Engineering
- For circular column minimum of 6 longitudinal bars are used.
- Plain cement concrete (PCC) this type of concrete is used on members-only when the tensile force is not acting on it.
- The floor area occupied by 50 kg of cement bag is 0.3m2 and height of 0.18 m.
- The volume of 50 kg of cement beg is 1.3 CFT.
- Cement more than 3 months old cannot be used for construction.
OTHER POSTS:
-
Useful Tips for Design of RCC Members | Beam, Column, Slab, Footing
-
General Specification for Residential Building | First, 2nd, 3rd & 4th Class
-
Basic Components of Building Structure | Building Elements
Cement shall be tested for its setting:
- The initial setting time shall not be less than 30 minutes.
- The final setting time shall not be more than 10 hours.
Civil Engineering Basic Knowledge for Concrete:
- The concrete should not be thrown from a height of 1m. Civil Engineering Notes
- Sand having a moisture content of more than 5% should be used for concrete mix.
- A cube test is carried out for each 30 cm3usage of concrete.
- Ready-mix concrete, the concrete is made at the factory and transported to the site, this type of concrete is used where there is a lack of space for mixing the concrete and used where a huge amount of concrete is required for construction.
- Adding more water in the concrete mix to increase setting time leads to the cracks or honeycomb in hardened concrete. Civil Engineering Notes
- The thickness of DPC Should not be less than 2.5 cm.
- Impermeability of concrete The concrete that resists the entry of water or moisture into it.
- The concrete can be lifted to a maximum height of 50m using concrete pumps. The curing period of RCC is 25 days. Civil Engineering Notes
- The Thermal expansion coefficients of concrete and steel are the same having value 12X10-6/Degree C.
- M20 grade concrete is generally used in the construction of the slab.
Slump IS 456:
Lightly reinforced 25 – 75 mm
Heavily reinforced 75 – 100 mm
Trench fill (insitu & Tremie) 100 – 150 mm (For Tremie no need of vibrator) Civil Engineering Notes
Curing Days Required:
Super Sulphate cement : 7 days
Ordinary Portland cement OPC : 10 days
Minerals and Admixture added cement : 14 days Civil Engineering Notes
Cube Samples:
1 – 5 M3: 1 No.
6 – 15 M3: 2 No’s
16 – 30 M3: 3 No’s
31 – 50 M3: 4 No’s
Above 50 M3: 4 + 1 No of addition sample for each 50 M3.

Grade of Concrete:
| Concrete Grade | Mix Ratio | Compressive Strength MPa ( N/mm²) | PSI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal Grade of Concrete | |||
| M5 | 1:5:10 | 05 MPa | 725 psi |
| M7.5 | 1: 4: 8 | 7.5 MPa | 1087 psi |
| M10 | 1 : 3: 6 | 10 MPa | 1450 psi |
| M15 | 1:2:4 | 15 MPa | 2175 psi |
| M20 | 1:1.5:3 | 20 MPa | 2900 psi |
| Standard Grade of Concrete | |||
| M25 | 1:1:2 | 25 MPa | 3625 psi |
| M30 | Design Mix | 30 MPa | 4350 psi |
| M35 | Design Mix | 35 MPa | 5075 psi |
| M40 | Design Mix | 40 MPa | 5800 psi |
| M45 | Design Mix | 45 MPa | 6525 psi |
| High Strength Concrete Grades | |||
| M50 | Design Mix | 50 MPa | 7250 psi |
| M55 | Design Mix | 55 MPa | 7975 psi |
| M60 | Design Mix | 60 MPa | 8700 psi |
| M65 | Design Mix | 65 MPa | 9425 psi |
| M70 | Design Mix | 70 MPa | 10150 psi |
Civil Engineering Basic Knowledge for Beam, Slab and Column:
- Hook length should not be less than 9D. Civil Engineering Notes
- Theodolite least count is 20 sec. where’s compass Least count is 30 mins.
- The length of each bar from the factory is 12 m.
- A head mason can work 25 to 30 #3 in the day. In construction, the rate analysis for the work of workers is calculated in Man-hours.
- Cantilever Beam has one fixed support and the other end is free, Simply supported beam has a minimum of two supports. Practical Knowledge of Civil Engineering
- Dead load is the self-weight of the structure.
- The height of the floor is usually 3m or 10ft.
- Vibration in freshly made concrete is done to remove the air bubble in the concrete mix.
- The minimum sill level height should be 44 inches.
- The transverse reinforcement provided in the column is called ties. And when they come in beams they called stirrups. Practical Knowledge of Civil Engineering
- Stirrups in beams and Ties in columns are provided to handle the shear force and to keep longitudinal bars in position. Civil Engineering Formulas
- Lapping of bars not allowed if the dia of the bar is more than 36 MM.
- The minimum thickness of the slab is 0.125m.
- The thickness of DPC Should not be less than 2.5 cm.
- Water PH values less than 6 should not be used for construction purposes.
- The prime reason for using steel as reinforcement is due to thermal expansion.

Civil Engineering Basic Knowledge for Good Stair:
Stairs give access from floor to floor. Stairs consists of a number of steps arranged in a single flight or more number of flights. The requirement of good stairs are describe as following : Civil Engineering Formulas
- Tread : Horizontal projection of a step in a stair case is called tread.. In residential buildings tread provided is 250 mm while in public buildings it is 270 mm to 300 mm.
The following empirical formula is used to decide rise and tread: 2 R + T > 550 mm but < 700 to 600 mm where R is riser in mm and T is tread in mm.
- Number of Steps in a Flight: Maximum number of steps in a flight should be limited to 12 to 14, while minimum is 3. Practical Knowledge of Civil Engineering
- Riser : Riser provided should be uniform. It is normally 150 mm to 175 mm in residential buildings while it is kept between 120 mm to 150 mm in public buildings. However in commercial buildings more rise is provided from the consideration of economic floor area. Civil Engineering Formulas
- Width : 0.9 m in residential buildings and 1.5 m to 2.5 m in public buildings.
- Hand Rails: Hand rails should be provided at a convenient height of a normal person which is from 850 mm to 900 mm.
- Head Room: Head room available in the stair case should not be less than 2.1 m.
- Slope: The slope or pitch of the stair should be between 25 degrees to 40 degrees. The rise in staris is in between 150mm to 200 mm. The Trade-in staircase is between 250 mm to 300 mm. Civil Engineering Formulas
Learn More
How To Calculate The Horizontal Distance Using With Auto Level Machine
Civil Engineering Basic Knowledge for Bricks:
- The number of bricks required for 1m3of brick masonry is 550 Bricks.
- The weight of first-class clay brick should be 3.85kg.
- Crushing strength of brick 10.5 MN/m2. Practical Knowledge of Civil Engineering
- The standard size of bricks is 19cm X 9Cm X 4Cm.
- Weight = 3.17 – 3.80 Kg
- Water absorption 12 to 15% Civil Engineering Formulas
- Compressive strength = 36Kn/cm2
- 230mm Wall/m3 = 460 Bricks + 20Cft Sand +66Kg Cement
Test of Building Materials:
Civil engineers should have proper knowledge of different tests of building materials.
- Soil test:- Core cutter test, Compaction test of soil, Sand replacement test, Tri-axial test, consolidation test, etc.
- Concrete test:- Slump test, compression test, split tensile test, soundness, etc.
- Bitumen test:- Ductility test, softening point test, gravity test, penetration test, etc. Read more about the bitumen test. Civil Engineering Formulas
Other Post
-
What is The Parapet Wall Purpose And Design Of Parapet Wall
-
How To Calculate The Length Of Roof Rafters
-
What is Sprayed Concrete in Concrete Construction
Civil Engineering Tips:
-
- Lapping of bars not allowed if the dia of bar is more than 36mm.
- For circular column minimum of 6 longitudinal bars are used.
- The minimum thickness of slab is 0.125m
- Water pH value less than 6 should not be used for construction purpose.
- The concrete Should not be thrown from a height more than 1m.
- The Compressive strength of Bricks is 3.5 N /mm2
- The initial setting time shall not be less than 30 minutes and the final setting time of cement is 10hours. Civil Engineering Formulas
- Dead Load means Self weight of Structure
- Sand having moisture content more than 5% should not be used for Concrete mix.
- DPC means Damp Proof Course. The thickness of DPC should not be less than 2.5cm.
- Cube test is carried out for each 30m3 usage of concrete.
- RMC : Ready Mix concrete, The concrete is made at factory and transported to the site, This type of concrete is used where there is a lack of space for mixing the concrete and used where a huge amount of concrete is required for construction.
- The height of floor is usually 3m or 10ft (If a person asks you whats the height of 12 storied building? Ans: 3m x 12floors = 36m)
- A head mason can work 25-30m3 in a day.
- In construction, the rate analysis for the work of workers is calculated in Man Hours. (Ex: 10$ for 1 Man hour)
- Cantilever Beam has One fixed support and the other end is free, Simply supported beam has a minimum of two supports. Civil Engineering Formulas
- PCC (Plain Cement Concrete) this type of concrete is used on members only when the tensile forces are not acting on it.
- The weight of first class clay brick should be 3.85 Kg. and it has a crushing strength of 10.5MN/m2
- Adding more water in the concrete mix to increase setting time leads to form the Cracks or honeycomb in hardened concrete.
- Vibration in freshly made concrete is done to remove the air bubbles in concrete mix.
- Impermeability of concrete: The concrete which resists the the entry of water or moisture into it.
- The concrete can be lifted to a maximum height of 50m using Concrete Pumps.
- The curing Period of RCC is 28days.
- The minimum sill level height should be 44 inches.
- The transverse reinforcement provided in columns are called Ties.
- The transverse reinforcement provided in Beams is called as Stirrups.
- Stirrups in Beams and Ties in Column are provided to handle the shear force and to keep longitudinal bars in position.
- The Prime reason for using steel as reinforcement is due to thermal expansion. The thermal expansion coefficient of concrete and steel is (approximately) same having value 12×10−6/°C
- M20 grade of concrete is generally used in the construction of slab.
- Weight of Bar is calculated using formula D2/162 (D = Dia of bar in mm)
- The No. of Bricks required for 1m3 of Brick masonary are 550 bricks.
- Specific gravity of Cement is 3.16g/cm3; Bricks is 2g/cm3; Sand is 2.65g/cm3 ,
- Standard Size of Brick is 19cm x 9cm x 4 cm or 19cm or 9cm x 9 cm
- Floor area occupied by 50kg of Cement bag is 0.3m2 and height of 0.18m.
- As per IS 456: 2000, Maximum dia of bar used in the slab should not exceed 1/8th of the total thickness of the slab.
- IS 456:2000 is Code of Practice for Plain and Reinforced Concrete
- IS 800:2000 is code of Practice for General steel construction
- The slope or Pitch of the stair should be in between 25 degrees to 40 degrees.
- The rise in stairs is in between 150mm to 200mm.
- Tread in staircase is in between 250mm to 300mm.
- Hook length should not be less than 9D (Dia of Bar)
- Unit weight of PCC is 24KN/m3 , RCC is 25 KN/m3 , Steel is 7850Kg/m3
- The volume of 50kg cement bag is 1.3CFT.
- Theodolite least count is 20Secs whereas Compass Least count is 30mins.
- TMT bars : TMT means Thermo Mechanically treated bars
- Cement more than 3 months old cannot be used for construction
- The length of each bar from factory is 12m.
Must Remember the Concrete Mix ratio of Different grades of Concrete at least till M20 grade of concrete:
| Concrete Grade | Mix Ratio |
| M5 | 1:5:10 |
| M7.5 | 1:4:8 |
| M10 | 1:3:6 |
| M15 | 1:2:4 |
| M20 | 1:1.5:3 |
| M25 | 1:1:2 |
| M30, M35, M40, M45, M50, M55, M60, M65, M70 | Design Mix |
Know about the Slump value of Concrete for Different concrete works:
| Concrete Mixes | Slump range in mm |
| Columns, Retaining walls | 75-150mm |
| Beams & Slabs | 50-100mm |
| CC Pavements | 20-30mm |
| Decks of bridge | 30-75mm |
| Vibrated Concrete | 12-25mm |
| Huge Mass constructions | 25-50mm |
Clear Cover to Main Reinforcement:
- FOOTINGS : 50 mm
- RAFT FOUNDATION.TOP : 50 mm
- RAFT FOUNDATION.BOTTOM/SIDES : 75 mm
- TRAP BEAM : 50 mm
- GRADE SLAB : 20 mm
- COLUMN : 40 mm
- SHEAR WALL : 25 mm
- BEAMS : 25 mm
- SLABS : 15 mm
- FLAT SLAB : 20 mm
- STAIRCASE : 15 mm
- RETAINING WALL : 20/ 25 mm on earth
- WATER RETAINING STRUCTURES : 20/30 mm
Other Post
-
How To Calculate The Cement Bags Required For 2000 sq. ft. House
-
How to Create The Design Of RCC Structures With Details
-
Methods of Concrete Column Repair for Damages and Cracks
Weight of Rod Per Meter Length:
DIA WEIGHT PER METER 6mm = 0.222Kg 8mm = 0.395 Kg 10mm = 0.616 Kg 12mm = 0.888 Kg 16mm = 1.578 Kg 20mm = 2.466 Kg 25mm = 3.853 Kg 32mm = 6.313 Kg 40mm = 9.865 Kg 1bag cement-50kg 1feet-0.3048m 1m-3.28ft 1sq.m-10.76sq.f t 1cu.m-35.31cu.ft 1acre-43560sq.ft 1hectare-2.47acre
Unit Weight of Different Materials:
- Concrete 25 kN/m3 Civil Engineering Tips
- Brick 19 kN/m3
- Steel 7850 Kg/m3
- Water 1000 Lt/m3
- Cement 1440 Kg/m3
- 1 Gallon 3.78 Litres
- Link 8″ = 200mm Civil Engineering Tips
- 1 Hectare 2.471 acr(10000m2)
- 1 Acr 4046.82m2 = 100 cent
Learn More
Civil Engineering Measurements And Conversion Factors
Development Length:
01. Compression 38d 02. Tension 47 & 60d 03. 1 Cent 435.60 Sft 04. 1 Meter 3.2808 ft 05. 1 M2 10.76 ft2 06. 1 Feet 0.3048m 07. 1 KN 100Kg 08. 1kN 1000N 09. 1 Ton 1000Kg = 10,000 N = 10 kN 10. 1 kG 9.81N Civil Engineering Tips
Civil Engineering Notes:
- Minimum thickness of slab is 125 mm.
- Water absorption should not be more than 15 %. Civil Engineering Tips
- Dimension tolerance for cubes + – 2 mm.
- Compressive strength of Bricks is 3.5 N /mm2
- Maximum Free fall of concrete allowed is 1.50 m. Civil Engineering Tips
- In soil filling as per IS code for every 100 sqm 3 sample for core cutting test should be taken.
- Electrical conduits shall not run in column
- Earth work excavation for basement above 3 m should be stepped form.
- Any back filling shall be compacted 95% of dry density at the optimum moisture content and in layers not more than 200mm for filling above structure and 300 mm for no structure
- A set of cube tests shall be carried out for each 30 cum of concrete / each levels of casting / each batch of cement.
- Water cement ratio for different grades of concrete shall not exceed 0.45 for M20 and above and 0.50 For M10 / M15 contractor
- For concrete grades M20 and above approved admixture shall be used as per mix design requirements.
- Cement shall be stored in dry places on a raised platform about 200mm above floor level and 300mm away from walls. Bags to be stacked not more than 10 bags high in such a manner that it is adequately protected from moisture and contamination.
- Samples from fresh concrete shall be taken and at least a set of 6 cubes of 150mm shall be prepared and cured. 3 Cubes each at 7 days and 28 days shall be tested for compressive strength. The test results should be submitted to engineer for approval. If results are unsatisfactory necessary action/rectification/remedial measures has to be exercised.
- Water used for both mixing and curing shall be clean and free from injurious amounts of oils, acids, alkalies, salts, sugar and organic materials or other substances that may be deleterious to concrete or steel. The ph. shall be generally between 6 and 8.
Learn More
Load Calculation On Column, Beam, Wall And Slab
Formula for Weight of Bar Calculation:
Weight of bar is calculated using formula D2/162 Where D= Dia of bar in mm
Common Abbreviation Used in Civil Engineering:
The common abbreviation used in civil engineering are as follows:
- A.A.S.H.T.O – American Association of State Highway Transport
- A.B – Anchor Bolt Or Asbestos Board
- A.C.I – American concrete institute.
- A.R.E.A – American Railway Engineering Association.
- A.S.C – Allowable stress of concrete.
- A.S.T.M – American Society for Testing Materials
- AC – Asphalt Concrete
- AE – Assistant Engineer
- APM – Assistant Project Manager
- B.M – Benchmark
- B.M – Bending moment.
- B.O.F – Bottom Of Foundation
- BHK – Bedroom, Hall, Kitchen
- BLK – Block Work
- BOQ – Bill Of Quantities
- BRW – Brick Retaining Wall
- BWK – Brick Work
- C.I.Pipe – Cast iron pipe.
- C.I.Sheet – Corrugated Iron sheet.
- CBW – Concrete Block Wall
- CC – Cement concrete.
- CC – Centre To Centre
- CE – Chief Engineer
- CIP – Cast In Place
- CJ – Construction Joint
- CL – Centre Line
- CMU – Concrete Masonry Unit
- CP – Cement plaster.
- CPM – Critical path method.
- CRW – Concrete Retaining Wall
- CS – Comparative statement.
- D – Diameter
- D.L – Dead load.
- Dia – Diameter
- DIM – Dimension
- DL – Development Length
- DPC – Damp proof course.
- DPR – Daily Progress Report
- DRG – Drawings
- DWLS – Dowels
- E.L – Environmental load.
- EGL – Existing ground level.
- EJ – Expansion Joint
- EL – Existing Load
- ELCB – Earth Leak Circuit Breaker
- F.M – Fineness Modulus.
- FGL – Formation ground level.
- FL – Floor Level
- FOC – Factor Of Safety
- Ft – Foot Or Feet
- GL – Ground Level
- GP – Ground plane.
- HAC – High Alumina Cement
- HFL – Highest flood level.
- HP – Horizontal plane.
- IOM – Inter Office Memo
- ISI – Indian Standard Institute.
- JE – Junior Engineer
- JST – Joist
- Kg – Kilogram.
- L.L – Live load.
- LC – Lime concrete.
- LW – Light Weight
- LWC – Light Weight Concrete
- M – Meter
- MB – Measurement book.
- MCB – Miniature Circuit Breaker
- MEP – Mechanical Electrical Plumbing
- MFL – Maximum Flood Level
- MM – Millimeter.
- MRC – Material Receipt Challan
- MT – Metric Tonnes
- N – Newton
- NCF – Neat cement finishing.
- OGL – Original ground level .
- OPC – Ordinary Portland Cement
- OSR – Open Soace Reservation Area
- PC – Pile Cap
- PC – Precast Concrete
- PCC – Plain Cement Concrete
- PERT – Programme Evaluation and Review Technique.
- PL – Plinth level.
- PM – Project Manager
- PO – Purchase Order
- PPE – Personal Protective Equipment
- PPR – Poly Propylene Random.
- PSF – Pound Per Square Foot
- PSI – Pound Per Square Inch
- PVC – Polyvinyl Chloride
- PWD – Permanent Works Engineer
- QC – Quality control
- QS – Quantity Surveyor
- R.B.W – Reinforced brick work.
- RBC – Reinforced Brick concrete.
- RC – Reinforced Concrete
- RCC – Reinforced Cement Concrete
- RL – Reduced level.
- RMC – Ready Mixed Concrete concrete.
- SCC – Self Compacting Concrete
- SRC – Sulphate Resisting Cement
- STP – Sewage Treatment Plant
- SWG – Standard wire gauge.
- TB – Tie Beam
- TBM – Tunnel Boring Machine
- TDS – Total Dissolved Solids
- TMT – Thermo Mechanical Treatment
- TOB – Top Of Beam
- TOC – Top Of Concrete
Learn More
-
Precautions to be Taken While Placing of Concrete | Do’s & Don’ts While Concreting
-
How to Calculate Quantities Cement, Sand, Aggregate and water in 1 m3 Concrete Work
-
What is 1.54 Constant for Concrete in Quantity Survey
Practical And Basic Knowledge of Civil Engineering
- U.S.C – Ultimate stress of concrete.
- UPVC – Unplasticized Polyvinyl chloride.
- USD – Ultimate strength design.
- VP – Vertical plane.
- W.C – Water closet.
- W.S.D – Working stress design.
- WL – Working Level
- WO – Work Order
Learn More
Civil Engineering Tips | Points to Remember For Civil Site Engineer
Conclusion:
Full article on Civil Engineering Basic Knowledge | Civil Engineering Tips| Civil Engineering Notes | Civil Engineering Formulas | Practical Knowledge of Civil Engineering. Thank you for the full reading of this article in “The Civil Engineering” platform in English. If you find this post helpful, then help others by sharing it on social media. If you have any question regarding article please tell me in comments.
Other Post
-
How To Calculate the Volume And Weight of Asphalt For Road Construction
-
Load Calculation On Column, Beam, Wall And Slab
-
Estimating Of Steel Bar Quantity for Construction
 Surveying & Architects A unique platform of Civil Engineering
Surveying & Architects A unique platform of Civil Engineering